3. Input File
To predict the structure of an amorphous material, one needs to prepare:
*.inpAn input file containing simulation parameters.*.xyzA file containing coordinates, connectivity, reactive sites, and force field information of a monomer.
In the following, we will describe how to prepare these files.
3.1. Simulation Parameters: *.inp
An input file mol.inp that containing all options is given below:
1charmm
2 scaling14 1.0 # Scaling factor of 1-4 electrostatic interactions.
3 rcutoff 12.0 # The cutoff radius for nonbonded interactions.
4 rswitch 10.0 # The distance to activate switching function. If it is
5 # larger than rcutoff, switching and shift function will not be used.
6 es_scheme ewald
7end
8
9opt
10 num_steps 500
11 epsilon 1.E-3
12end
13
14md
15 dt 0.0005 # The time step in ps.
16 temp 1400. # The temperature in Kelvin.
17 temp_nhc_length 5 # The length of temperature Nose-Hoover chain.
18 temp_nhc_tau 0.05 # The time constant of temperature Nose-Hoover chain in ps.
19 num_steps 1000 # The number of steps.
20 output_freq 10000 # The output frequency.
21end
22
23unit
24 a.xyz 30
25 b.xyz 40
26end
27
28grow
29 dir_fn paf80 # The folder to store intermediate files.
30 md_freq 20 # The frequency to do MD simulations.
31 num_steps 10 # The number of steps to grow. -1: Just after all species are depleted.
32 r_intra 4 # The distance to activate intramolecular bonding.
33end
The simulation is controlled by parameters in mol.inp. There are some points here:
You can put as many spaces as you wish anywhere.
Anything after
#is regarded as comment.A statement block like
md...endis called an option block, anddt 0.001is an option to setdta value of0.001. If not given, a default number will be assigned.
You can find explainations for all details in All Option Keywords. In practise, you can just copy the above file and modify some options.
3.2. Monomer Information: *.xyz
A typical monomer file monomer.xyz is given below:
145
2PAF-
3 C -0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
4 C -0.99204361 0.67989624 -0.94006954
5 C -1.62513076 -0.10642738 -1.90138442
6 C -1.24520505 2.04367646 -0.93242437
7 C -2.50784698 0.45009463 -2.80643536
8 H -1.41636178 -1.16636581 -1.94027187
9 C -2.12863118 2.60280511 -1.84215854
10 H -0.74872619 2.68691666 -0.22165626
11 C -2.76733728 1.81056951 -2.77756466
12 H -2.99072901 -0.17871632 -3.54031416
13 H -2.31214042 3.66730700 -1.81823226
14 H -3.45545629 2.24898711 -3.48516956
15 C 0.67989624 0.99204361 0.94006954
16 C 2.04367646 1.24520505 0.93242437
17 C -0.10642738 1.62513076 1.90138442
18 C 2.60280511 2.12863118 1.84215854
19 H 2.68691666 0.74872619 0.22165626
20 C 0.45009463 2.50784698 2.80643536
21 H -1.16636581 1.41636178 1.94027187
22 C 1.81056951 2.76733728 2.77756466
23 H 3.66730700 2.31214042 1.81823226
24 H -0.17871632 2.99072901 3.54031416
25 H 2.24898711 3.45545629 3.48516956
26 C 0.99204361 -0.67989624 -0.94006954
27 C 1.24520505 -2.04367646 -0.93242437
28 C 1.62513076 0.10642738 -1.90138442
29 C 2.12863118 -2.60280511 -1.84215854
30 H 0.74872619 -2.68691666 -0.22165626
31 C 2.50784698 -0.45009463 -2.80643536
32 H 1.41636178 1.16636581 -1.94027187
33 C 2.76733728 -1.81056951 -2.77756466
34 H 2.31214042 -3.66730700 -1.81823226
35 H 2.99072901 0.17871632 -3.54031416
36 H 3.45545629 -2.24898711 -3.48516956
37 C -0.67989624 -0.99204361 0.94006954
38 C 0.10642738 -1.62513076 1.90138442
39 C -2.04367646 -1.24520505 0.93242437
40 C -0.45009463 -2.50784698 2.80643536
41 H 1.16636581 -1.41636178 1.94027187
42 C -2.60280511 -2.12863118 1.84215854
43 H -2.68691666 -0.74872619 0.22165626
44 C -1.81056951 -2.76733728 2.77756466
45 H 0.17871632 -2.99072901 3.54031416
46 H -3.66730700 -2.31214042 1.81823226
47 H -2.24898711 -3.45545629 3.48516956
48
49 1 2 1.0 13 1.0 24 1.0 35 1.0
50 2 3 1.5 4 1.5
51 3 5 1.5 6 1.0
52 4 7 1.5 8 1.0
53 5 9 1.5 10 1.0
54 6
55 7 9 1.5 11 1.0
56 8
57 9 12 1.0
58 10
59 11
60 12
61 13 14 1.5 15 1.5
62 14 16 1.5 17 1.0
63 15 18 1.5 19 1.0
64 16 20 1.5 21 1.0
65 17
66 18 20 1.5 22 1.0
67 19
68 20 23 1.0
69 21
70 22
71 23
72 24 25 1.5 26 1.5
73 25 27 1.5 28 1.0
74 26 29 1.5 30 1.0
75 27 31 1.5 32 1.0
76 28
77 29 31 1.5 33 1.0
78 30
79 31 34 1.0
80 32
81 33
82 34
83 35 36 1.5 37 1.5
84 36 38 1.5 39 1.0
85 37 40 1.5 41 1.0
86 38 42 1.5 43 1.0
87 39
88 40 42 1.5 44 1.0
89 41
90 42 45 1.0
91 43
92 44
93 45
94
95 9 0 12 0 9 0 12 0 0
96 20 0 23 0 20 0 23 0 0
97 31 0 34 0 31 0 34 0 0
98 42 0 45 0 42 0 45 0 0
99
100 CG331 0.0
101 CG2R61 0.0
102 CG2R61 -0.115000
103 CG2R61 -0.115000
104 CG2R61 -0.115000
105 HGR61 +0.115000
106 CG2R61 -0.115000
107 HGR61 +0.115000
108 CG2R61 -0.115000
109 HGR61 +0.115000
110 HGR61 +0.115000
111 HGR61 +0.115000
112 CG2R61 0.0
113 CG2R61 -0.115000
114 CG2R61 -0.115000
115 CG2R61 -0.115000
116 HGR61 +0.115000
117 CG2R61 -0.115000
118 HGR61 +0.115000
119 CG2R61 -0.115000
120 HGR61 +0.115000
121 HGR61 +0.115000
122 HGR61 +0.115000
123 CG2R61 0.0
124 CG2R61 -0.115000
125 CG2R61 -0.115000
126 CG2R61 -0.115000
127 HGR61 +0.115000
128 CG2R61 -0.115000
129 HGR61 +0.115000
130 CG2R61 -0.115000
131 HGR61 +0.115000
132 HGR61 +0.115000
133 HGR61 +0.115000
134 CG2R61 0.0
135 CG2R61 -0.115000
136 CG2R61 -0.115000
137 CG2R61 -0.115000
138 HGR61 +0.115000
139 CG2R61 -0.115000
140 HGR61 +0.115000
141 CG2R61 -0.115000
142 HGR61 +0.115000
143 HGR61 +0.115000
144 HGR61 +0.115000
There are 4 parts in the monomer file:
Line 1-47: Monomer coordinates in XYZ format: number of atoms; an arbitrary title; element symbol and coordiantes in Angstrom.
Line 48: A blank line.
Line 49-93: Connectivity. This is the Gaussian job file (gjf) format. For example,
18 20 1.5 22 1.0means that atom18connects with atom20and22with a bond order of1.5and1.0, respectively. Currently, the bond order is not used by ABPolymer.Line 94: A blank line.
Line 95-98: Reactive sties. They are the atoms that are ready to react with other ones to generate a new bond. This molecule has 4 reactive sites, so there are 4 line. A reactive site is defined as:
bonding_atom_indices_A 0 leaving_atom_indices_A 0 bonding_atom_indices_B 0 leaving_atom_indices_B 0 site_type
Let’s take line 97 as an example. During a reaction, some atoms are leaving and some atoms are bonding to others, this is given by leaving_atom_indices_A and bonding_atom_indices_A, respectively. They are seperated by 0. As shown below, the hydrogen atom 34 is leaving and the carbon atom 31 will be bonding with other atoms, so we write 31 0 34 0.
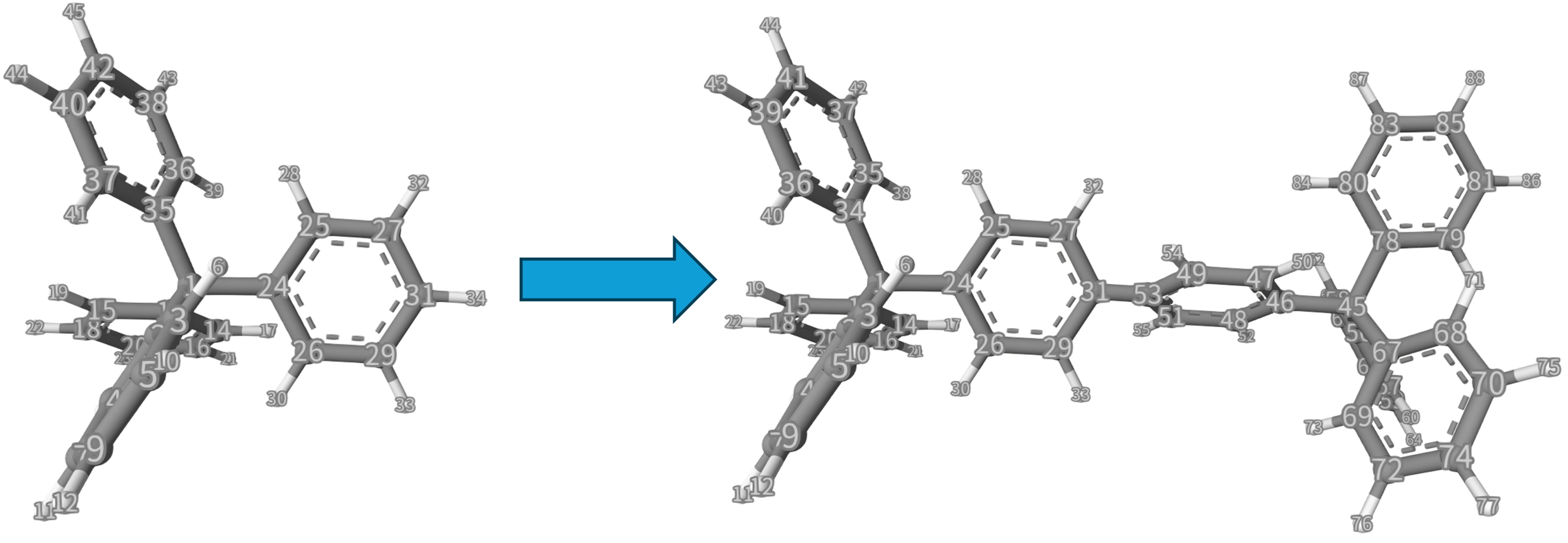
To be compatible with some functions that are being developed, this information has to be repeated once, so we write 31 0 34 0 31 0 34 0
Finally, each site will be given an integer as a type. An important point is that two sites can bond only when the sum of their types are zero! For example, the above site is 0, so they can bond to each other.
In the following case, if we have two species, we can set the types of the sites for +1 and -1, so only the contraction reaction will occur, avoiding the non-chemical reactions. Note that, for the amine, we set two leaving atoms.
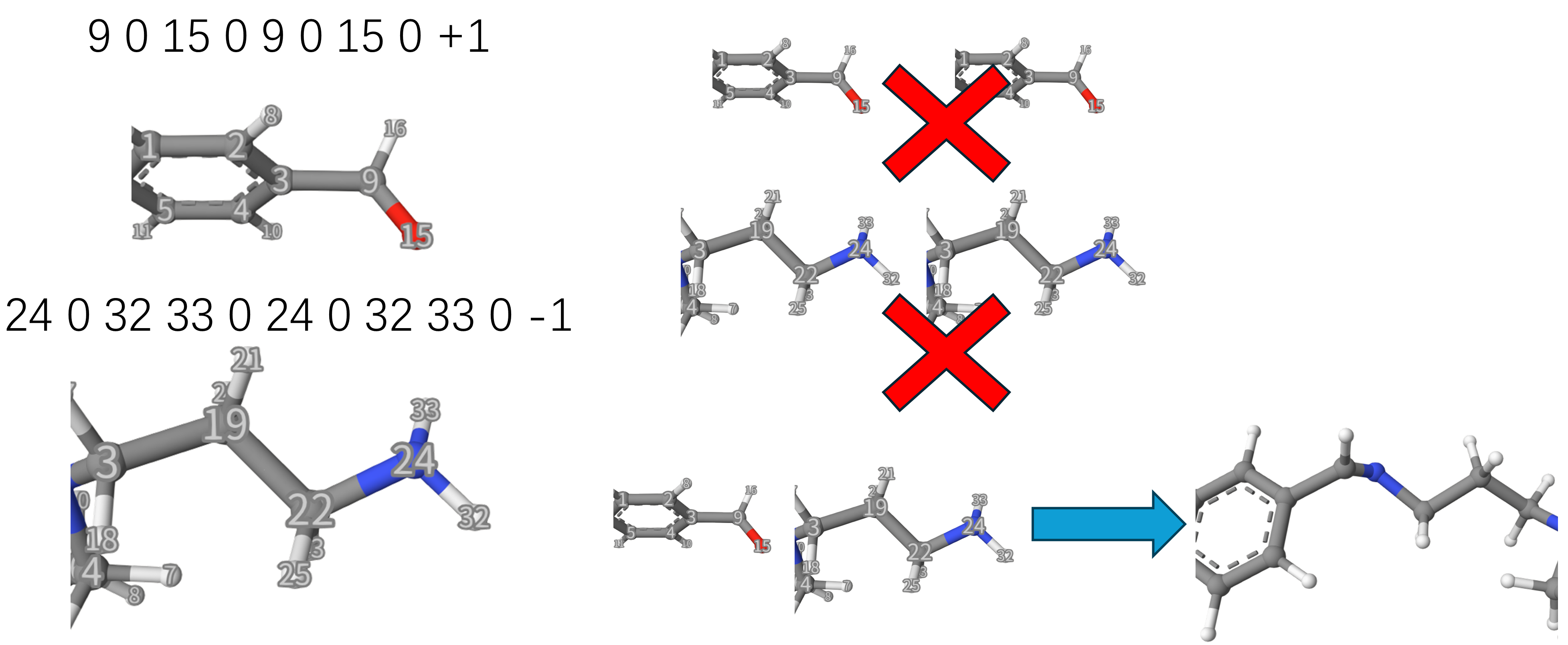
Line 99: A blank line.
Line 100-144: Force field information. Each line corresponds to each atom defined in coordinate part. For example,
CG2R61 -0.115000means that this atom is ofCG2R61type and has a charge of-0.115000.
For details of preparing monomer file *.xyz, like how to determine the atom types, how to calculate atomic charges, and how to generate connectivity automatically, see Monomer File Preparation.