5. Monomer File Preparation
TODOTODOTODOTODOTOD
Here, we describe how to prepare a reasonable monomer file step-by-step.
5.1. Coordinate
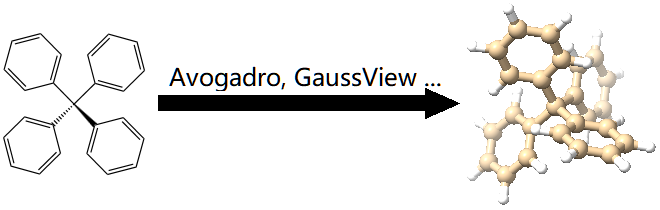
Given a monomer, like the one shown below, there are a lot of tools in computational chemistry community to build its 3D structure, like Avogadro or GaussView. The structure can be then optimized at some quantum chemical level of theory, like xTB or B3LYPD3/def2-SVP. The obtained structure should be saved in XYZ format, like monomer.inp shown below.
145
2monomer
3C -0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
4C -0.99204361 0.67989624 -0.94006954
5C -1.62513076 -0.10642738 -1.90138442
6C -1.24520505 2.04367646 -0.93242437
7C -2.50784698 0.45009463 -2.80643536
8H -1.41636178 -1.16636581 -1.94027187
9C -2.12863118 2.60280511 -1.84215854
10H -0.74872619 2.68691666 -0.22165626
11C -2.76733728 1.81056951 -2.77756466
12H -2.99072901 -0.17871632 -3.54031416
13H -2.31214042 3.66730700 -1.81823226
14H -3.45545629 2.24898711 -3.48516956
15C 0.67989624 0.99204361 0.94006954
16C 2.04367646 1.24520505 0.93242437
17C -0.10642738 1.62513076 1.90138442
18C 2.60280511 2.12863118 1.84215854
19H 2.68691666 0.74872619 0.22165626
20C 0.45009463 2.50784698 2.80643536
21H -1.16636581 1.41636178 1.94027187
22C 1.81056951 2.76733728 2.77756466
23H 3.66730700 2.31214042 1.81823226
24H -0.17871632 2.99072901 3.54031416
25H 2.24898711 3.45545629 3.48516956
26C 0.99204361 -0.67989624 -0.94006954
27C 1.24520505 -2.04367646 -0.93242437
28C 1.62513076 0.10642738 -1.90138442
29C 2.12863118 -2.60280511 -1.84215854
30H 0.74872619 -2.68691666 -0.22165626
31C 2.50784698 -0.45009463 -2.80643536
32H 1.41636178 1.16636581 -1.94027187
33C 2.76733728 -1.81056951 -2.77756466
34H 2.31214042 -3.66730700 -1.81823226
35H 2.99072901 0.17871632 -3.54031416
36H 3.45545629 -2.24898711 -3.48516956
37C -0.67989624 -0.99204361 0.94006954
38C 0.10642738 -1.62513076 1.90138442
39C -2.04367646 -1.24520505 0.93242437
40C -0.45009463 -2.50784698 2.80643536
41H 1.16636581 -1.41636178 1.94027187
42C -2.60280511 -2.12863118 1.84215854
43H -2.68691666 -0.74872619 0.22165626
44C -1.81056951 -2.76733728 2.77756466
45H 0.17871632 -2.99072901 3.54031416
46H -3.66730700 -2.31214042 1.81823226
47H -2.24898711 -3.45545629 3.48516956
5.2. Connectivity
When we have obtained coordinates, the easiest way to generate remaining information is to use the tool topgen, which is a part of ABCluster suite of software. For user’s convenience, we have already included it in the distribution of ABGrow. Just run the following command:
$ topgen monomer.xyz
You will get the following output:
Analyze topology for the molecule from "monomer.xyz" ... done.
Exporting results to "monomer" +
.gjf: GJF file with bonding information.
-cycles.txt: Containing cycle texts that can be used for ABCluster:geom calculation.
-bonding.xyz: XYZ file with bonding information for ABCluster:geom calculation.
-rigid.xyz: XYZ file with bonding information for ABCluster:rigidmol calculation.
.psf: PSF file with topology information for ABCluster:geom/NAMD calculations.
-abgrow.xyz: XYZ file with much information for ABGrow calculation.
In "monomer-rigid.xyz", "monomer-abgrow.xyz", and "monomer.psf":
"X" means unknown atomic type.
Total charge: -0.3900
-----------------------------------------------------------
| You can adjust charges to meet the target total charge, |
| or re-fit RESP charges using, e.g., Multiwfn. |
-----------------------------------------------------------
Atoms are typed using graph representation learning. Please cite:
Zhang, J. Atom Typing Using Graph Representation Learning: How Do Models Learn Chemistry?
J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 156, 204108
Attention
If you used topgen, please cite the following paper:
Zhang, J. Atom Typing Using Graph Representation Learning: How Do Models Learn Chemistry? J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 156, 204108.
Although topgen generates a lot of files, the only one useful to us is monomer-abgrow.xyz:
145
2Generated by ABCluster
3C -0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
4C -0.99204361 0.67989624 -0.94006954
5C -1.62513076 -0.10642738 -1.90138442
6C -1.24520505 2.04367646 -0.93242437
7C -2.50784698 0.45009463 -2.80643536
8H -1.41636178 -1.16636581 -1.94027187
9C -2.12863118 2.60280511 -1.84215854
10H -0.74872619 2.68691666 -0.22165626
11C -2.76733728 1.81056951 -2.77756466
12H -2.99072901 -0.17871632 -3.54031416
13H -2.31214042 3.66730700 -1.81823226
14H -3.45545629 2.24898711 -3.48516956
15C 0.67989624 0.99204361 0.94006954
16C 2.04367646 1.24520505 0.93242437
17C -0.10642738 1.62513076 1.90138442
18C 2.60280511 2.12863118 1.84215854
19H 2.68691666 0.74872619 0.22165626
20C 0.45009463 2.50784698 2.80643536
21H -1.16636581 1.41636178 1.94027187
22C 1.81056951 2.76733728 2.77756466
23H 3.66730700 2.31214042 1.81823226
24H -0.17871632 2.99072901 3.54031416
25H 2.24898711 3.45545629 3.48516956
26C 0.99204361 -0.67989624 -0.94006954
27C 1.24520505 -2.04367646 -0.93242437
28C 1.62513076 0.10642738 -1.90138442
29C 2.12863118 -2.60280511 -1.84215854
30H 0.74872619 -2.68691666 -0.22165626
31C 2.50784698 -0.45009463 -2.80643536
32H 1.41636178 1.16636581 -1.94027187
33C 2.76733728 -1.81056951 -2.77756466
34H 2.31214042 -3.66730700 -1.81823226
35H 2.99072901 0.17871632 -3.54031416
36H 3.45545629 -2.24898711 -3.48516956
37C -0.67989624 -0.99204361 0.94006954
38C 0.10642738 -1.62513076 1.90138442
39C -2.04367646 -1.24520505 0.93242437
40C -0.45009463 -2.50784698 2.80643536
41H 1.16636581 -1.41636178 1.94027187
42C -2.60280511 -2.12863118 1.84215854
43H -2.68691666 -0.74872619 0.22165626
44C -1.81056951 -2.76733728 2.77756466
45H 0.17871632 -2.99072901 3.54031416
46H -3.66730700 -2.31214042 1.81823226
47H -2.24898711 -3.45545629 3.48516956
48
491 2 1.0 13 1.0 24 1.0 35 1.0
502 3 1.0 4 2.0
513 5 2.0 6 1.0
524 7 2.0 8 1.0
535 9 2.0 10 1.0
546
557 9 2.0 11 1.0
568
579 12 1.0
5810
5911
6012
6113 14 2.0 15 1.0
6214 16 2.0 17 1.0
6315 18 2.0 19 1.0
6416 20 2.0 21 1.0
6517
6618 20 2.0 22 1.0
6719
6820 23 1.0
6921
7022
7123
7224 25 2.0 26 1.0
7325 27 2.0 28 1.0
7426 29 2.0 30 1.0
7527 31 2.0 32 1.0
7628
7729 31 2.0 33 1.0
7830
7931 34 1.0
8032
8133
8234
8335 36 1.0 37 2.0
8436 38 2.0 39 1.0
8537 40 2.0 41 1.0
8638 42 2.0 43 1.0
8739
8840 42 2.0 44 1.0
8941
9042 45 1.0
9143
9244
9345
94
95<< Add Reactive Sites by User >>
96
97CG2RC7 0.0700
98CG2R61 -0.1150
99CG2R61 -0.1150
100CG2R61 -0.1150
101CG2R61 -0.1150
102HGR61 0.1150
103CG2R61 -0.1150
104HGR61 0.1150
105CG2R61 -0.1150
106HGR61 0.1150
107HGR61 0.1150
108HGR61 0.1150
109CG2R61 -0.1150
110CG2R61 -0.1150
111CG2R61 -0.1150
112CG2R61 -0.1150
113HGR61 0.1150
114CG2R61 -0.1150
115HGR61 0.1150
116CG2R61 -0.1150
117HGR61 0.1150
118HGR61 0.1150
119HGR61 0.1150
120CG2R61 -0.1150
121CG2R61 -0.1150
122CG2R61 -0.1150
123CG2R61 -0.1150
124HGR61 0.1150
125CG2R61 -0.1150
126HGR61 0.1150
127CG2R61 -0.1150
128HGR61 0.1150
129HGR61 0.1150
130HGR61 0.1150
131CG2R61 -0.1150
132CG2R61 -0.1150
133CG2R61 -0.1150
134CG2R61 -0.1150
135HGR61 0.1150
136CG2R61 -0.1150
137HGR61 0.1150
138CG2R61 -0.1150
139HGR61 0.1150
140HGR61 0.1150
141HGR61 0.1150
Line 49-93 is connectivity information of Gaussian job file (gjf) format, which was explained in Input File. In most cases, the connectivity is reliable.
Bond orders do not matter as long as is greater than 0. For example, GaussView may generate a file that atom 35 and 37 has a bond order of 1.5, being different from what we got by topgen as line 83 suggests a bond order of 2.0. This will not affect the following simulation.
Although monomer-abgrow.xyz has already contained much information, we still have to add or check the following information.
5.3. Reactive Sites
Reactive sites are the atoms to react in the formation of amorphous materials. For a reactive site, one atom is to form a new bond and one atom is to leave, like the one shown below:
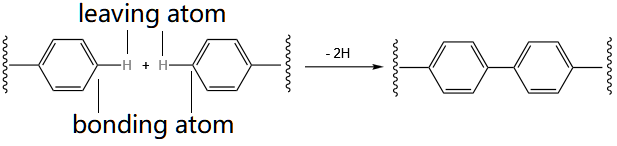
For each reactive site, they can be defined in the following manner:
bonding_atom_index leaving_atom_index 0 0
where the 2 0 are reserved for future use. Since there are 4 reactive sites (see below)
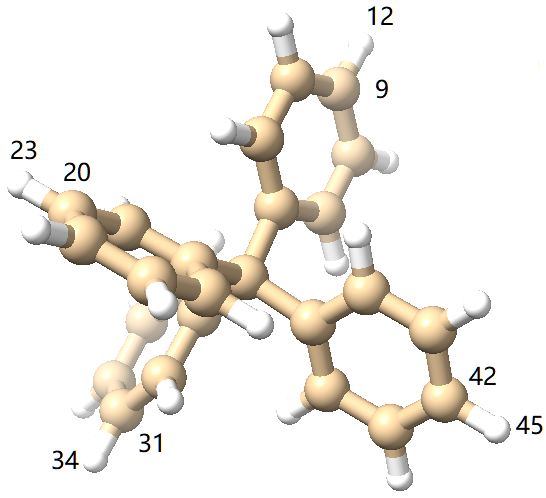
we add them and arrive at the following monomer file:
145
2Generated by ABCluster
3C -0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
4C -0.99204361 0.67989624 -0.94006954
5C -1.62513076 -0.10642738 -1.90138442
6C -1.24520505 2.04367646 -0.93242437
7C -2.50784698 0.45009463 -2.80643536
8H -1.41636178 -1.16636581 -1.94027187
9C -2.12863118 2.60280511 -1.84215854
10H -0.74872619 2.68691666 -0.22165626
11C -2.76733728 1.81056951 -2.77756466
12H -2.99072901 -0.17871632 -3.54031416
13H -2.31214042 3.66730700 -1.81823226
14H -3.45545629 2.24898711 -3.48516956
15C 0.67989624 0.99204361 0.94006954
16C 2.04367646 1.24520505 0.93242437
17C -0.10642738 1.62513076 1.90138442
18C 2.60280511 2.12863118 1.84215854
19H 2.68691666 0.74872619 0.22165626
20C 0.45009463 2.50784698 2.80643536
21H -1.16636581 1.41636178 1.94027187
22C 1.81056951 2.76733728 2.77756466
23H 3.66730700 2.31214042 1.81823226
24H -0.17871632 2.99072901 3.54031416
25H 2.24898711 3.45545629 3.48516956
26C 0.99204361 -0.67989624 -0.94006954
27C 1.24520505 -2.04367646 -0.93242437
28C 1.62513076 0.10642738 -1.90138442
29C 2.12863118 -2.60280511 -1.84215854
30H 0.74872619 -2.68691666 -0.22165626
31C 2.50784698 -0.45009463 -2.80643536
32H 1.41636178 1.16636581 -1.94027187
33C 2.76733728 -1.81056951 -2.77756466
34H 2.31214042 -3.66730700 -1.81823226
35H 2.99072901 0.17871632 -3.54031416
36H 3.45545629 -2.24898711 -3.48516956
37C -0.67989624 -0.99204361 0.94006954
38C 0.10642738 -1.62513076 1.90138442
39C -2.04367646 -1.24520505 0.93242437
40C -0.45009463 -2.50784698 2.80643536
41H 1.16636581 -1.41636178 1.94027187
42C -2.60280511 -2.12863118 1.84215854
43H -2.68691666 -0.74872619 0.22165626
44C -1.81056951 -2.76733728 2.77756466
45H 0.17871632 -2.99072901 3.54031416
46H -3.66730700 -2.31214042 1.81823226
47H -2.24898711 -3.45545629 3.48516956
48
491 2 1.0 13 1.0 24 1.0 35 1.0
502 3 1.0 4 2.0
513 5 2.0 6 1.0
524 7 2.0 8 1.0
535 9 2.0 10 1.0
546
557 9 2.0 11 1.0
568
579 12 1.0
5810
5911
6012
6113 14 2.0 15 1.0
6214 16 2.0 17 1.0
6315 18 2.0 19 1.0
6416 20 2.0 21 1.0
6517
6618 20 2.0 22 1.0
6719
6820 23 1.0
6921
7022
7123
7224 25 2.0 26 1.0
7325 27 2.0 28 1.0
7426 29 2.0 30 1.0
7527 31 2.0 32 1.0
7628
7729 31 2.0 33 1.0
7830
7931 34 1.0
8032
8133
8234
8335 36 1.0 37 2.0
8436 38 2.0 39 1.0
8537 40 2.0 41 1.0
8638 42 2.0 43 1.0
8739
8840 42 2.0 44 1.0
8941
9042 45 1.0
9143
9244
9345
94
95 9 12 0 0
9620 23 0 0
9731 34 0 0
9842 45 0 0
99
100CG2RC7 0.0700
101CG2R61 -0.1150
102CG2R61 -0.1150
103CG2R61 -0.1150
104CG2R61 -0.1150
105HGR61 0.1150
106CG2R61 -0.1150
107HGR61 0.1150
108CG2R61 -0.1150
109HGR61 0.1150
110HGR61 0.1150
111HGR61 0.1150
112CG2R61 -0.1150
113CG2R61 -0.1150
114CG2R61 -0.1150
115CG2R61 -0.1150
116HGR61 0.1150
117CG2R61 -0.1150
118HGR61 0.1150
119CG2R61 -0.1150
120HGR61 0.1150
121HGR61 0.1150
122HGR61 0.1150
123CG2R61 -0.1150
124CG2R61 -0.1150
125CG2R61 -0.1150
126CG2R61 -0.1150
127HGR61 0.1150
128CG2R61 -0.1150
129HGR61 0.1150
130CG2R61 -0.1150
131HGR61 0.1150
132HGR61 0.1150
133HGR61 0.1150
134CG2R61 -0.1150
135CG2R61 -0.1150
136CG2R61 -0.1150
137CG2R61 -0.1150
138HGR61 0.1150
139CG2R61 -0.1150
140HGR61 0.1150
141CG2R61 -0.1150
142HGR61 0.1150
143HGR61 0.1150
144HGR61 0.1150
5.4. Force Field Information
The last part of monomer input file is the force field information. For each atom, its “atom type” and “charge” are given:
...
CG2R61 -0.1150
CG2R61 -0.1150
HGR61 0.1150
CG2R61 -0.1150
...
Unfortunately, it is not possible to get 100% correct force field information automatically, so manually adjustment and calculation is still needed.
5.4.1. Atom Type
In the current version of ABGrow, each atom will be given an “atom type” as indicated in CGenFF, i.e. the following part in par_all36_cgenff.prm:
we add them and arrive at the following monomer file:
1ATOMS
2!hydrogens
3MASS -1 HGA1 1.00800 ! alphatic proton, CH
4MASS -1 HGA2 1.00800 ! alphatic proton, CH2
5MASS -1 HGA3 1.00800 ! alphatic proton, CH3
6MASS -1 HGA4 1.00800 ! alkene proton; RHC=
7MASS -1 HGA5 1.00800 ! alkene proton; H2C=CR
8MASS -1 HGA6 1.00800 ! aliphatic H on fluorinated C, monofluoro
9MASS -1 HGA7 1.00800 ! aliphatic H on fluorinated C, difluoro
10MASS -1 HGAAM0 1.00800 ! aliphatic H, NEUTRAL trimethylamine (#)
11MASS -1 HGAAM1 1.00800 ! aliphatic H, NEUTRAL dimethylamine (#)
12MASS -1 HGAAM2 1.00800 ! aliphatic H, NEUTRAL methylamine (#)
13!(#) EXTREME care is required when doing atom typing on compounds that look like this. Use ONLY
14!on NEUTRAL METHYLAMINE groups, NOT Schiff Bases, but DO use on 2 out of 3 guanidine nitrogens
15MASS -1 HGP1 1.00800 ! polar H
16MASS -1 HGP2 1.00800 ! polar H, +ve charge
17MASS -1 HGP3 1.00800 ! polar H, thiol
18MASS -1 HGP4 1.00800 ! polar H, neutral conjugated -NH2 group (NA bases)
19MASS -1 HGP5 1.00800 ! polar H on quarternary ammonium salt (choline)
20MASS -1 HGPAM1 1.00800 ! polar H, NEUTRAL dimethylamine (#), terminal alkyne H
21MASS -1 HGPAM2 1.00800 ! polar H, NEUTRAL methylamine (#)
22MASS -1 HGPAM3 1.00800 ! polar H, NEUTRAL ammonia (#)
23!(#) EXTREME care is required when doing atom typing on compounds that look like this. Use ONLY
24!on NEUTRAL METHYLAMINE groups, NOT Schiff Bases, but DO use on 2 out of 3 guanidine nitrogens
25MASS -1 HGR51 1.00800 ! nonpolar H, neutral 5-mem planar ring C, LJ based on benzene
26MASS -1 HGR52 1.00800 ! Aldehyde H, formamide H (RCOH); nonpolar H, neutral 5-mem planar ring C adjacent to heteroatom or + charge
27MASS -1 HGR53 1.00800 ! nonpolar H, +ve charge HIS he1(+1)
28MASS -1 HGR61 1.00800 ! aromatic H
29MASS -1 HGR62 1.00800 ! nonpolar H, neutral 6-mem planar ring C adjacent to heteroatom
30MASS -1 HGR63 1.00800 ! nonpolar H, NAD+ nicotineamide all ring CH hydrogens
31MASS -1 HGR71 1.00800 ! nonpolar H, neutral 7-mem arom ring, AZUL, azulene, kevo
32!carbons
33MASS -1 CG1T1 12.01100 ! internal alkyne R-C#C
34MASS -1 CG1T2 12.01100 ! terminal alkyne H-C#C
35MASS -1 CG1N1 12.01100 ! C for cyano group
36MASS -1 CG2D1 12.01100 ! alkene; RHC= ; imine C
37MASS -1 CG2D2 12.01100 ! alkene; H2C=
38MASS -1 CG2D1O 12.01100 ! double bond C adjacent to heteroatom. In conjugated systems, the atom to which it is double bonded must be CG2DC1.
39MASS -1 CG2D2O 12.01100 ! double bond C adjacent to heteroatom. In conjugated systems, the atom to which it is double bonded must be CG2DC2.
40MASS -1 CG2DC1 12.01100 ! conjugated alkenes, R2C=CR2
41MASS -1 CG2DC2 12.01100 ! conjugated alkenes, R2C=CR2
42MASS -1 CG2DC3 12.01100 ! conjugated alkenes, H2C=
43MASS -1 CG2N1 12.01100 ! conjugated C in guanidine/guanidinium
44MASS -1 CG2N2 12.01100 ! conjugated C in amidinium cation
45MASS -1 CG2O1 12.01100 ! carbonyl C: amides
46MASS -1 CG2O2 12.01100 ! carbonyl C: esters, [neutral] carboxylic acids
47MASS -1 CG2O3 12.01100 ! carbonyl C: [negative] carboxylates
48MASS -1 CG2O4 12.01100 ! carbonyl C: aldehydes
49MASS -1 CG2O5 12.01100 ! carbonyl C: ketones
50MASS -1 CG2O6 12.01100 ! carbonyl C: urea, carbonate
51MASS -1 CG2O7 12.01100 ! CO2 carbon
52MASS -1 CG2R51 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring, his CG, CD2(0), trp
53MASS -1 CG2R52 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring, double bound to N, PYRZ, pyrazole
54MASS -1 CG2R53 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring, double bound to N and adjacent to another heteroatom, purine C8, his CE1 (0,+1), 2PDO, kevo
55MASS -1 CG2R57 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring, bipyrroles
56MASS -1 CG25C1 12.01100 ! same as CG2DC1 but in 5-membered ring with exocyclic double bond
57MASS -1 CG25C2 12.01100 ! same as CG2DC2 but in 5-membered ring with exocyclic double bond
58MASS -1 CG251O 12.01100 ! same as CG2D1O but in 5-membered ring with exocyclic double bond
59MASS -1 CG252O 12.01100 ! same as CG2D2O but in 5-membered ring with exocyclic double bond
60MASS -1 CG2R61 12.01100 ! 6-mem aromatic C
61MASS -1 CG2R62 12.01100 ! 6-mem aromatic C for protonated pyridine (NIC) and rings containing carbonyls (see CG2R63) (NA)
62MASS -1 CG2R63 12.01100 ! 6-mem aromatic amide carbon (NA) (and other 6-mem aromatic carbonyls?)
63MASS -1 CG2R64 12.01100 ! 6-mem aromatic amidine and guanidine carbon (between 2 or 3 Ns and double-bound to one of them), NA, PYRM
64MASS -1 CG2R66 12.01100 ! 6-mem aromatic carbon bound to F
65MASS -1 CG2R67 12.01100 ! 6-mem aromatic carbon of biphenyl
66MASS -1 CG2RC0 12.01100 ! 6/5-mem ring bridging C, guanine C4,C5, trp
67MASS -1 CG2R71 12.01100 ! 7-mem ring arom C, AZUL, azulene, kevo
68MASS -1 CG2RC7 12.01100 ! sp2 ring connection with single bond(!), AZUL, azulene, kevo
69MASS -1 CG301 12.01100 ! aliphatic C, no hydrogens, neopentane
70MASS -1 CG302 12.01100 ! aliphatic C, no hydrogens, trifluoromethyl
71MASS -1 CG311 12.01100 ! aliphatic C with 1 H, CH
72MASS -1 CG312 12.01100 ! aliphatic C with 1 H, difluoromethyl
73MASS -1 CG314 12.01100 ! aliphatic C with 1 H, adjacent to positive N (PROT NTER) (+)
74MASS -1 CG321 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for CH2
75MASS -1 CG322 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for CH2, monofluoromethyl
76MASS -1 CG323 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for CH2, thiolate carbon
77MASS -1 CG324 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for CH2, adjacent to positive N (piperidine) (+)
78MASS -1 CG331 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for methyl group (-CH3)
79MASS -1 CG334 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for methyl group (-CH3), adjacent to positive N (PROT NTER) (+)
80MASS -1 CG3AM0 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for CH3, NEUTRAL trimethylamine methyl carbon (#)
81MASS -1 CG3AM1 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for CH3, NEUTRAL dimethylamine methyl carbon (#)
82MASS -1 CG3AM2 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for CH3, NEUTRAL methylamine methyl carbon (#)
83!(#) EXTREME care is required when doing atom typing on compounds that look like this. Use ONLY
84!on NEUTRAL METHYLAMINE groups, NOT ETHYL, NOT Schiff Bases, but DO use on 2 out of 3 guanidine nitrogens
85MASS -1 CG3C31 12.01100 ! cyclopropyl carbon
86MASS -1 CG3C41 12.01100 ! cyclobutyl carbon
87MASS -1 CG3C50 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring aliphatic quaternary C (cholesterol, bile acids)
88MASS -1 CG3C51 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring aliphatic CH (proline CA, furanoses)
89MASS -1 CG3C52 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring aliphatic CH2 (proline CB/CG/CD, THF, deoxyribose)
90MASS -1 CG3C53 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring aliphatic CH adjacent to positive N (proline.H+ CA) (+)
91MASS -1 CG3C54 12.01100 ! 5-mem ring aliphatic CH2 adjacent to positive N (proline.H+ CD) (+)
92MASS -1 CG3RC1 12.01100 ! bridgehead in bicyclic systems containing at least one 5-membered or smaller ring
93!(+) Includes protonated Shiff base (NG3D5, NG2R52 in 2HPP) but NOT amidinium (NG2R52 in IMIM), guanidinium
94!nitrogens
95MASS -1 NG1T1 14.00700 ! N for cyano group
96!MASS -1 NG1D1 14.00700 ! terminal N in azides, lsk
97MASS -1 NG2D1 14.00700 ! N for neutral imine/Schiff's base (C=N-R, acyclic amidine, gunaidine)
98MASS -1 NG2S0 14.00700 ! N,N-disubstituted amide, proline N (CO=NRR')
99MASS -1 NG2S1 14.00700 ! peptide nitrogen (CO=NHR)
100MASS -1 NG2S2 14.00700 ! terminal amide nitrogen (CO=NH2)
101MASS -1 NG2S3 14.00700 ! external amine ring nitrogen (planar/aniline), phosphoramidate
102!MASS -1 NG2S4 14.00700 ! neutral hydroxamic acid
103MASS -1 NG2O1 14.00700 ! NITB, nitrobenzene
104MASS -1 NG2P1 14.00700 ! N for protonated imine/Schiff's base (C=N(+)H-R, acyclic amidinium, guanidinium)
105MASS -1 NG2R43 14.00700 ! amide in 4-memebered ring (planar), AZDO, lsk
106MASS -1 NG2R50 14.00700 ! double bound neutral 5-mem planar ring, purine N7
107MASS -1 NG2R51 14.00700 ! single bound neutral 5-mem planar (all atom types sp2) ring, his, trp pyrrole (fused)
108MASS -1 NG2R52 14.00700 ! protonated schiff base, amidinium, guanidinium in 5-membered ring, HIS, 2HPP, kevo
109MASS -1 NG2R53 14.00700 ! amide in 5-memebered NON-SP2 ring (slightly pyramidized), 2PDO, kevo
110MASS -1 NG2R57 14.00700 ! 5-mem ring, bipyrroles
111MASS -1 NG2R60 14.00700 ! double bound neutral 6-mem planar ring, pyr1, pyzn
112MASS -1 NG2R61 14.00700 ! single bound neutral 6-mem planar ring imino nitrogen; glycosyl linkage
113MASS -1 NG2R62 14.00700 ! double bound 6-mem planar ring with heteroatoms in o or m, pyrd, pyrm
114MASS -1 NG2R67 14.00700 ! 6-mem planar ring substituted with 6-mem planar ring (N-phenyl pyridinones etc.)
115MASS -1 NG2RC0 14.00700 ! 6/5-mem ring bridging N, indolizine, INDZ, kevo
116MASS -1 NG301 14.00700 ! neutral trimethylamine nitrogen
117MASS -1 NG311 14.00700 ! neutral dimethylamine nitrogen
118MASS -1 NG321 14.00700 ! neutral methylamine nitrogen
119MASS -1 NG331 14.00700 ! neutral ammonia nitrogen
120MASS -1 NG3C51 14.00700 ! secondary sp3 amine in 5-membered ring
121MASS -1 NG3N1 14.00700 ! N in hydrazine, HDZN
122MASS -1 NG3P0 14.00700 ! quarternary N+, choline
123MASS -1 NG3P1 14.00700 ! tertiary NH+ (PIP)
124MASS -1 NG3P2 14.00700 ! secondary NH2+ (proline)
125MASS -1 NG3P3 14.00700 ! primary NH3+, phosphatidylethanolamine
126!oxygens
127MASS -1 OG2D1 15.99940 ! carbonyl O: amides, esters, [neutral] carboxylic acids, aldehydes, uera
128MASS -1 OG2D2 15.99940 ! carbonyl O: negative groups: carboxylates, carbonate
129MASS -1 OG2D3 15.99940 ! carbonyl O: ketones
130MASS -1 OG2D4 15.99940 ! 6-mem aromatic carbonyl oxygen (nucleic bases)
131MASS -1 OG2D5 15.99940 ! CO2 oxygen
132MASS -1 OG2N1 15.99940 ! NITB, nitrobenzene
133MASS -1 OG2P1 15.99940 ! =O in phosphate or sulfate
134MASS -1 OG2R50 15.99940 ! FURA, furan
135MASS -1 OG3R60 15.99940 ! O in 6-mem cyclic enol ether (PY01, PY02) or ester
136MASS -1 OG301 15.99940 ! ether -O- !SHOULD WE HAVE A SEPARATE ENOL ETHER??? IF YES, SHOULD WE MERGE IT WITH OG3R60???
137MASS -1 OG302 15.99940 ! ester -O-
138MASS -1 OG303 15.99940 ! phosphate/sulfate ester oxygen
139MASS -1 OG304 15.99940 ! linkage oxygen in pyrophosphate/pyrosulphate
140MASS -1 OG311 15.99940 ! hydroxyl oxygen
141MASS -1 OG312 15.99940 ! ionized alcohol oxygen
142MASS -1 OG3C31 15.99940 ! epoxide oxygen, 1EOX, 1BOX, sc
143MASS -1 OG3C51 15.99940 ! 5-mem furanose ring oxygen (ether)
144MASS -1 OG3C61 15.99940 ! DIOX, dioxane, ether in 6-membered ring !SHOULD WE MERGE THIS WITH OG3R60???
145!sulphurs
146MASS -1 SG2D1 32.06000 ! thiocarbonyl S
147MASS -1 SG2R50 32.06000 ! THIP, thiophene
148MASS -1 SG311 32.06000 ! sulphur, SH, -S-
149MASS -1 SG301 32.06000 ! sulfur C-S-S-C type
150MASS -1 SG302 32.06000 ! thiolate sulfur (-1)
151MASS -1 SG3O1 32.06000 ! sulfate -1 sulfur
152MASS -1 SG3O2 32.06000 ! neutral sulfone/sulfonamide sulfur
153MASS -1 SG3O3 32.06000 ! neutral sulfoxide sulfur
154!halogens
155MASS -1 CLGA1 35.45300 ! CLET, DCLE, chloroethane, 1,1-dichloroethane
156MASS -1 CLGA3 35.45300 ! TCLE, 1,1,1-trichloroethane
157MASS -1 CLGR1 35.45300 ! CHLB, chlorobenzene
158MASS -1 BRGA1 79.90400 ! BRET, bromoethane
159MASS -1 BRGA2 79.90400 ! DBRE, 1,1-dibromoethane
160MASS -1 BRGA3 79.90400 ! TBRE, 1,1,1-dibromoethane
161MASS -1 BRGR1 79.90400 ! BROB, bromobenzene
162MASS -1 IGR1 126.90447 ! IODB, iodobenzene
163MASS -1 FGA1 18.99800 ! aliphatic fluorine, monofluoro
164MASS -1 FGA2 18.99800 ! aliphatic fluorine, difluoro
165MASS -1 FGA3 18.99800 ! aliphatic fluorine, trifluoro
166MASS -1 FGP1 18.99800 ! anionic F, for ALF4 AlF4-
167MASS -1 FGR1 18.99800 ! aromatic flourine
The third column, like HGA1 or CG331, is the atom type that can be accepted by ABGrow. Statements after ! are the explainations of that atom type. For example,
MASS -1 CG331 12.01100 ! aliphatic C for methyl group (-CH3)
So, for a carbon atom that is aliphatic C for methyl group (-CH3), it should be given a type of CG331.
In most cases, topgen can predict the correct type, but sometimes it fails. For exmaple, in Line 100, the first carbone atom is given a type of CG2RC7, which is of course wrong. This is a quaternary carbon with 4 benzene rings. Unfortunately, CGenFF does not have such an atom type. In this circumstance, one should give it a type from CGenFF that is chemically most similar. We can find this:
MASS -1 CG301 12.01100 ! aliphatic C, no hydrogens, neopentane
This quaternary carbon type in neopentane seems to be the most similar one. So, this carbon atom is given a type of CG301. Remeber to make this change in monomer-abgrow.xyz.
5.4.2. Charge
The automatically generated atomic charges usually do not work. A quatnum chemical calculation is needed. There are 2 steps:
Generate wave function file with a quantum chemical program, like Qbics (free of charge) or Gaussian (commercial software).
Calculate RESP charges with Multiwfn.
5.4.2.1. Generate Wave Function
For the purpose of calculating RESP charges, a density functional theory (DFT) like B3LYP/6-31g(d) is often sufficient.
An input file for Qbics monomer.inp is given below:
1basis
2 6-31g(d)
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0 # The total charge.
7 spin2p1 1 # The spin multiplicity.
8end
9
10mol
11 monomer-abgrow.xyz # You can add path to the file name, or just put all coordinates here.
12end
13
14task
15 energy b3lyp
16end
Then run Qbics to do the calculation:
$ qbics-linux-cpu monomer.inp -n 8 > monomer.out &
If you use Windows version, just change qbics-linux-cpu to qbics-win-cpu; -+n 8 menas 8 cores are used, which can be changed to other suitable number. After calculation, you can get a file called monomer.mwfn. This is the wave function file that can be supported by Multiwfn best.
For more details of Qbics, please refer to http://qibcs.info. A tutorial can be found at http://qibcs.info/tutorial.
If you prefer Gaussian, prepare the following input monomer.gjf:
1%nprocs=8
2#B3LYP/6-31g(d) Output(wfn)
3
4monomer
5
60 1
7C -0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
8C -0.99204361 0.67989624 -0.94006954
9C -1.62513076 -0.10642738 -1.90138442
10C -1.24520505 2.04367646 -0.93242437
11C -2.50784698 0.45009463 -2.80643536
12H -1.41636178 -1.16636581 -1.94027187
13C -2.12863118 2.60280511 -1.84215854
14H -0.74872619 2.68691666 -0.22165626
15C -2.76733728 1.81056951 -2.77756466
16H -2.99072901 -0.17871632 -3.54031416
17H -2.31214042 3.66730700 -1.81823226
18H -3.45545629 2.24898711 -3.48516956
19C 0.67989624 0.99204361 0.94006954
20C 2.04367646 1.24520505 0.93242437
21C -0.10642738 1.62513076 1.90138442
22C 2.60280511 2.12863118 1.84215854
23H 2.68691666 0.74872619 0.22165626
24C 0.45009463 2.50784698 2.80643536
25H -1.16636581 1.41636178 1.94027187
26C 1.81056951 2.76733728 2.77756466
27H 3.66730700 2.31214042 1.81823226
28H -0.17871632 2.99072901 3.54031416
29H 2.24898711 3.45545629 3.48516956
30C 0.99204361 -0.67989624 -0.94006954
31C 1.24520505 -2.04367646 -0.93242437
32C 1.62513076 0.10642738 -1.90138442
33C 2.12863118 -2.60280511 -1.84215854
34H 0.74872619 -2.68691666 -0.22165626
35C 2.50784698 -0.45009463 -2.80643536
36H 1.41636178 1.16636581 -1.94027187
37C 2.76733728 -1.81056951 -2.77756466
38H 2.31214042 -3.66730700 -1.81823226
39H 2.99072901 0.17871632 -3.54031416
40H 3.45545629 -2.24898711 -3.48516956
41C -0.67989624 -0.99204361 0.94006954
42C 0.10642738 -1.62513076 1.90138442
43C -2.04367646 -1.24520505 0.93242437
44C -0.45009463 -2.50784698 2.80643536
45H 1.16636581 -1.41636178 1.94027187
46C -2.60280511 -2.12863118 1.84215854
47H -2.68691666 -0.74872619 0.22165626
48C -1.81056951 -2.76733728 2.77756466
49H 0.17871632 -2.99072901 3.54031416
50H -3.66730700 -2.31214042 1.81823226
51H -2.24898711 -3.45545629 3.48516956
52
53monomer.wfn
Then run Gaussian to do the calculation:
$ g16 < monomer.gjf > monomer.out &
After calculation, you can get a file called monomer.wfn. This is the wave function file that can be supported by Multiwfn best.
5.4.2.2. Calculate RESP Charges
With monomer.mwfn or monomer.wfn, restrained electrostatic potential (RESP) can be evaluated easily with powerful and free Multiwfn. You can run the following commands:
$ Multiwfn monomer.mwfn
$ 7 # Choose: Population analysis and calculation of atomic charges
$ 18 # Choose: Restrained ElectroStatic Potential (RESP) atomic charge
$ 1 # Choose: Start standard two-stage RESP fitting calculation
$ y # Save RESP charges to monomer.chg.
Attention
If you used Multiwfn to calculate RESP charges, please cite the following papers:
Zhang, J.; Lu, T. Efficient Evaluation of Electrostatic Potential with Computerized Optimized Code Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 20323.
Zhang, J. libreta: Computerized Optimization and Code Synthesis for Electron Repulsion Integral Evaluation J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2018, 14, 572.
Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A Multifunctional Wavefunction Analyzer J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580.
After a few minutes, RESP charges will be saved to monomer.chg. Open it you will see:
1C 0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 -1.5653348594
2C -0.992044 0.679896 -0.940070 0.5486338023
3C -1.625131 -0.106427 -1.901384 -0.1807938321
4C -1.245205 2.043676 -0.932424 -0.1757742630
5C -2.507847 0.450095 -2.806435 -0.1528019340
6H -1.416362 -1.166366 -1.940272 0.1381451620
7C -2.128631 2.602805 -1.842159 -0.1687077518
8H -0.748726 2.686917 -0.221656 0.1232876422
9C -2.767337 1.810570 -2.777565 -0.1093811603
10H -2.990729 -0.178716 -3.540314 0.1236800912
11...
The last column is the charges. Use them to replace the charges in monomer-abgrow.xyz, you will get a good monomer file:
145
2RESP at B3LYP/6-31g(d)
3C -0.00000000 0.00000000 0.00000000
4C -0.99204361 0.67989624 -0.94006954
5C -1.62513076 -0.10642738 -1.90138442
6C -1.24520505 2.04367646 -0.93242437
7C -2.50784698 0.45009463 -2.80643536
8H -1.41636178 -1.16636581 -1.94027187
9C -2.12863118 2.60280511 -1.84215854
10H -0.74872619 2.68691666 -0.22165626
11C -2.76733728 1.81056951 -2.77756466
12H -2.99072901 -0.17871632 -3.54031416
13H -2.31214042 3.66730700 -1.81823226
14H -3.45545629 2.24898711 -3.48516956
15C 0.67989624 0.99204361 0.94006954
16C 2.04367646 1.24520505 0.93242437
17C -0.10642738 1.62513076 1.90138442
18C 2.60280511 2.12863118 1.84215854
19H 2.68691666 0.74872619 0.22165626
20C 0.45009463 2.50784698 2.80643536
21H -1.16636581 1.41636178 1.94027187
22C 1.81056951 2.76733728 2.77756466
23H 3.66730700 2.31214042 1.81823226
24H -0.17871632 2.99072901 3.54031416
25H 2.24898711 3.45545629 3.48516956
26C 0.99204361 -0.67989624 -0.94006954
27C 1.24520505 -2.04367646 -0.93242437
28C 1.62513076 0.10642738 -1.90138442
29C 2.12863118 -2.60280511 -1.84215854
30H 0.74872619 -2.68691666 -0.22165626
31C 2.50784698 -0.45009463 -2.80643536
32H 1.41636178 1.16636581 -1.94027187
33C 2.76733728 -1.81056951 -2.77756466
34H 2.31214042 -3.66730700 -1.81823226
35H 2.99072901 0.17871632 -3.54031416
36H 3.45545629 -2.24898711 -3.48516956
37C -0.67989624 -0.99204361 0.94006954
38C 0.10642738 -1.62513076 1.90138442
39C -2.04367646 -1.24520505 0.93242437
40C -0.45009463 -2.50784698 2.80643536
41H 1.16636581 -1.41636178 1.94027187
42C -2.60280511 -2.12863118 1.84215854
43H -2.68691666 -0.74872619 0.22165626
44C -1.81056951 -2.76733728 2.77756466
45H 0.17871632 -2.99072901 3.54031416
46H -3.66730700 -2.31214042 1.81823226
47H -2.24898711 -3.45545629 3.48516956
48
491 2 1.0 13 1.0 24 1.0 35 1.0
502 3 1.0 4 2.0
513 5 2.0 6 1.0
524 7 2.0 8 1.0
535 9 2.0 10 1.0
546
557 9 2.0 11 1.0
568
579 12 1.0
5810
5911
6012
6113 14 2.0 15 1.0
6214 16 2.0 17 1.0
6315 18 2.0 19 1.0
6416 20 2.0 21 1.0
6517
6618 20 2.0 22 1.0
6719
6820 23 1.0
6921
7022
7123
7224 25 2.0 26 1.0
7325 27 2.0 28 1.0
7426 29 2.0 30 1.0
7527 31 2.0 32 1.0
7628
7729 31 2.0 33 1.0
7830
7931 34 1.0
8032
8133
8234
8335 36 1.0 37 2.0
8436 38 2.0 39 1.0
8537 40 2.0 41 1.0
8638 42 2.0 43 1.0
8739
8840 42 2.0 44 1.0
8941
9042 45 1.0
9143
9244
9345
94
95 9 12 0 0
9620 23 0 0
9731 34 0 0
9842 45 0 0
99
100CG301 -1.5653348594
101CG2R61 0.5486338023
102CG2R61 -0.1807938321
103CG2R61 -0.1757742630
104CG2R61 -0.1528019340
105HGR61 0.1381451620
106CG2R61 -0.1687077518
107HGR61 0.1232876422
108CG2R61 -0.1093811603
109HGR61 0.1236800912
110HGR61 0.1285771475
111HGR61 0.1146450489
112CG2R61 0.5537613777
113CG2R61 -0.1776415775
114CG2R61 -0.1804809560
115CG2R61 -0.1693787789
116HGR61 0.1236576037
117CG2R61 -0.1536901781
118HGR61 0.1379626861
119CG2R61 -0.1094535255
120HGR61 0.1289189567
121HGR61 0.1239239689
122HGR61 0.1147394315
123CG2R61 0.5556504140
124CG2R61 -0.1789253746
125CG2R61 -0.1816910129
126CG2R61 -0.1694062811
127HGR61 0.1245726781
128CG2R61 -0.1538736680
129HGR61 0.1381249369
130CG2R61 -0.1091800778
131HGR61 0.1289147407
132HGR61 0.1241384965
133HGR61 0.1146368563
134CG2R61 0.5523475596
135CG2R61 -0.1836196251
136CG2R61 -0.1777055806
137CG2R61 -0.1519120037
138HGR61 0.1384408466
139CG2R61 -0.1680540950
140HGR61 0.1240363984
141CG2R61 -0.1104475731
142HGR61 0.1240069731
143HGR61 0.1285444303
144HGR61 0.1149068592
At Line 2, we have made the title more informative.
This is the final monomer file we need.