Tip
All input files can be downloaded: Files.
TSO-DFT (2): Diabatic States
This tutorial will lead you step by step to do target state optimization DFT (TSO-DFT) using Qbics. TSO-DFT is an originally developed method in Qbics. It is a powerful and accurate method for excited and diabatic states. In many physical processes like charge transfer, TSO-DFT can give much more reasonable results than TDDFT. Therefore, it is worth learning this method.
Hint
If you use Qbics to do TSO-DFT in you paper, please cite the following references:
In this tutorial, we will introduce how to use TSO-DFT to study dibatic states.
Example: Definition of Diabatic States of NaCl
What is a diabatic state? Its exact definition can be found in textbooks but are not relevant to us here. Here we just use an example to show what a diabatic state is. We will take NaCl molecule as an example.
Adiabatic State
We will calculate the ground state of NaCl at B3LYP/def2-TZVP level of theory:
1basis
2 def2-tzvp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 1
8 type U
9end
10
11mol
12 Na 0.0 0.0 -0.68381052
13 Cl 0.0 0.0 1.68381052
14end
15
16task
17 energy b3lyp
18end
Let us check the Mulliken charges in nacl-1.out:
1Mulliken Populations
2====================
3 # Symbol Charge Spin
4----------------------------------------------
5 1 Na 0.64773687 -0.00000889
6 2 Cl -0.64773687 0.00000889
7----------------------------------------------
8 Sum -0.00000000 0.00000000
9----------------------------------------------
10...omitted...
11Final total energy: -622.60503718 Hartree
Therefore, the Mulliken charges are 0.6477 and -0.6477, respectively, so the charges are delocalzied over the whole molecule. This state is also called adiabatic state.
Diabatic State: [Na+][Cl-]
Intuitively, one may think that NaCl is composed of a sodium cation Na+ and a chloride antion Cl-. However, as shown above, in the adiabatic state, charges are delocalized over the molecule. Is it possible to calculate a state that charges are forced to localize on some atoms? Such state is called diabatic state. In the following, we will calculate a diabatic state of [Na+][Cl-]:
1basis
2 def2-tzvp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 1
8 type U # This is needed for TSO-DFT.
9 no_scf tso
10end
11
12scfguess
13 type fragden
14 frag +1 1 1
15 frag -1 1 2
16end
17
18mol
19 Na 0.0 0.0 -0.68381052
20 Cl 0.0 0.0 1.68381052
21end
22
23task
24 energy b3lyp
25end
You can see that, in scfguess...end, we are setting a superposition of fragment density (fragden) as SCF initial guess. The only difference is that we set no_scf tso in scf...end:
frag +1 1 1We are seeting the fragment of atom1with charge+1and spin multiplicity1. See scfguess for details.frag -1 1 2We are seeting the fragment of atom2with charge-1and spin multiplicity1.
After calculation, in nacl-2.out, we can find this:
1Mulliken Populations
2====================
3 # Symbol Charge Spin
4----------------------------------------------
5 1 Na 1.00000000 0.00000000
6 2 Cl -1.00000000 -0.00000000
7----------------------------------------------
8 Sum -0.00000000 -0.00000000
9----------------------------------------------
10...omitted...
11Final total energy: -622.58940107 Hartree
Indeed, at Na and Cl atom, the Mulliken charge is 1.00 and -1.00, respectively, in line with our assumed diabatic state [Na+][Cl-]. Its is higher than the adiabatic state by
-622.58940107 - (-622.60503718) = 0.0156 Hartree = 9.81 kcal/mol
Actually, this is the so-called charge-transfer interaction energy. By the way, if you check the SCF process of this diabatic state:
1 #it SCF energy 2e energy |deltaE| |deltaP| Orbital Time/second
2---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
3 1 -622.57645781 318.90071152 1.950E-01 1.100E-05 guess 0.046
4 2 -622.58412894 319.42032296 7.671E-03 3.461E-05 diis 0.054
5 3 -622.58935124 319.21103043 5.222E-03 3.376E-05 diis 0.052
6 4 -622.58939707 319.19096764 4.584E-05 5.708E-06 diis 0.052
7 5 -622.58939958 319.18902943 2.506E-06 9.746E-07 diis 0.051
8 6 -622.58940082 319.19159833 1.235E-06 3.969E-07 diis 0.053
9 7 -622.58940107 319.19461843 2.492E-07 9.841E-08 diis 0.052
10---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
11 Great (^ _ ^) SCF has converged in 7 iterations. (0.367 seconds)
The energy difference of the first and last cycle
-622.58940107 - (-622.57645781) = 0.0129 Hartree = 8.12 kcal/mol
is the so-called polarization interaction enerrgy.
Energy Decomposition Analysis of [Na+][Cl-]
To check this, if you do an EDA (see Energy Decomposition Analysis) for [Na+][Cl-] with the following input:
1basis
2 def2-tzvp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 1
8 type U # This is needed for TSO-DFT.
9end
10
11eda
12 type tso
13 frag +1 1 1
14 frag -1 1 2
15end
16
17mol
18 Na 0.0 0.0 -0.68381052
19 Cl 0.0 0.0 1.68381052
20end
21
22task
23 eda b3lyp
24end
In the output nacl-eda.out:
1WITHOUT BSSE correction:
2Electrostatic interaction energy: -146.30 kcal/mol
3Exchange-correlation interaction energy: 23.91 kcal/mol
4Polarization interaction energy: -8.12 kcal/mol
5Charge transfer interaction energy: -9.81 kcal/mol
6Grimme's dispersion interaction: 0.00 kcal/mol
7----------------------------------------------------------------
8Total interaction energy: -140.33 kcal/mol
Here, Charge transfer interaction energy: -9.81 kcal/mol and Polarization interaction energy: -8.12 kcal/mol confirm our previous calculations.
Diabatic State: [Na][Cl]
Besides [Na+][Cl-], we can also assume another diabatic state: NaCl is composed of 2 neutral radical:
1basis
2 def2-tzvp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 1
8 type U # This is needed for TSO-DFT.
9 no_scf tso
10end
11
12scfguess
13 type fragden
14 frag 0 2 1
15 frag 0 -2 2
16end
17
18mol
19 Na 0.0 0.0 -0.68381052
20 Cl 0.0 0.0 1.68381052
21end
22
23task
24 energy b3lyp
25end
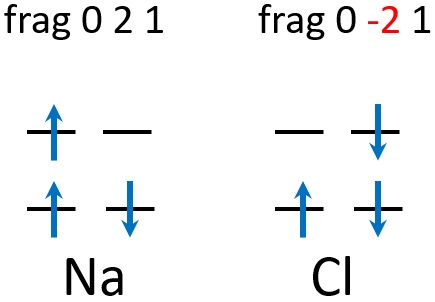
Here, frag 0 2 1 means that Na has a single alpha electron, while frag 0 2 1 means that Cl has a single beta electron, like this:
After calculation, we can find this in nacl-3.out:
1---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2 #it SCF energy 2e energy |deltaE| |deltaP| Orbital Time/second
3---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 1 -622.42824748 316.12630594 3.002E-02 3.077E-04 guess 0.051
5 2 -622.43470909 315.62361860 6.462E-03 2.354E-04 diis 0.063
6 3 -622.43589868 315.69293084 1.190E-03 2.159E-05 diis 0.057
7 4 -622.43598379 315.69186515 8.511E-05 2.740E-05 diis 0.059
8 5 -622.43599795 315.67167823 1.417E-05 5.266E-07 diis 0.057
9 6 -622.43600008 315.68068350 2.120E-06 9.311E-06 diis 0.071
10 7 -622.43600052 315.68009817 4.407E-07 5.151E-07 diis 0.057
11---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
12...omitted...
13Mulliken Populations
14====================
15 # Symbol Charge Spin
16----------------------------------------------
17 1 Na -0.00000000 0.50000000
18 2 Cl 0.00000000 -0.50000000
19----------------------------------------------
20 Sum -0.00000000 -0.00000000
21----------------------------------------------
22...omitted..
23Final total energy: -622.43600052 Hartree
So, the polarization and charge transfer interaction energy is:
-622.43600052 - (-622.42824748) Hartree = -4.88 kcal/mol
-622.60503718 - (-622.43600052) Hartree = -106.07 kcal/mol
Compared with [Na+][Cl-], the charge transfer energy of [Na][Cl] is extremely high.
You can also try to compute a diabatic state of [Na-][Cl+] if you wish.
In practise, to study diabatic states of molecular dimer or clusters, you can simply use eda since all needed calculations will be done automatically. You just need to set the fragment charges and spin multiplicities.
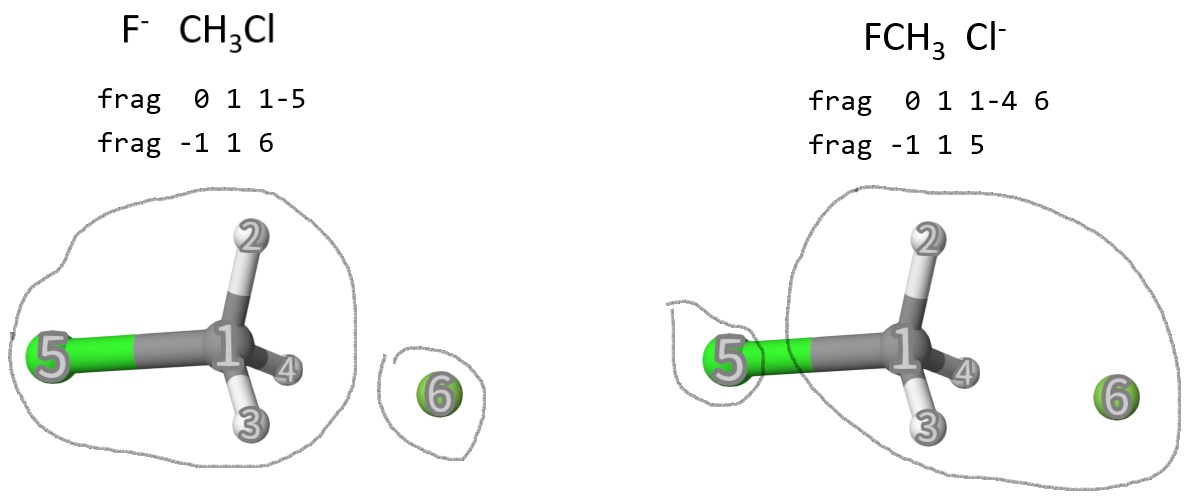
Example: Reactant and Product Diabatic States of F-+CH3Cl
Reactant Complex
Now we consider the reaction F-+CH3Cl. First, we calculate the reactant complex. Now we calculate the reactant and product diabatic state:
1basis
2 def2-svp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 -1
8 type U # This is needed for TSO-DFT.
9 no_scf tso
10end
11
12scfguess
13 type fragden
14 frag 0 1 1-5
15 frag -1 1 6
16end
17
18mol
19 C -0.43654823 1.13197968 0.00000000
20 H -0.07987539 1.63637787 0.87365150
21 H -0.07987539 1.63637787 -0.87365150
22 H -1.50654823 1.13199286 0.00000000
23 Cl 0.15009830 -0.52737135 0.00000000
24 F -1.63124586 2.75454539 -0.44024554
25end
26
27task
28 energy b3lyp
29end
1basis
2 def2-svp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 -1
8 type U # This is needed for TSO-DFT.
9 no_scf tso
10end
11
12scfguess
13 type fragden
14 frag 0 1 1-4 6
15 frag -1 1 5
16end
17
18mol
19 C -0.43654823 1.13197968 0.00000000
20 H -0.07987539 1.63637787 0.87365150
21 H -0.07987539 1.63637787 -0.87365150
22 H -1.50654823 1.13199286 0.00000000
23 Cl 0.15009830 -0.52737135 0.00000000
24 F -1.63124586 2.75454539 -0.44024554
25end
26
27task
28 energy b3lyp
29end
The two dibatic states can be set using frag:
Transition State
In the same way, we calculate the reactant and product diabatic states, but at the transition state:
1basis
2 def2-svp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 -1
8 type U # This is needed for TSO-DFT.
9 no_scf tso
10end
11
12scfguess
13 type fragden
14 frag 0 1 1-5
15 frag -1 1 6
16end
17
18mol
19 C -0.59663490 1.29366556 -0.07171644
20 H -0.18159761 1.68969864 0.84430018
21 H -0.12252870 1.52677601 -1.01427388
22 H -1.59298434 0.87532545 -0.06612308
23 Cl 0.43269073 -0.72181312 0.13298792
24 F -1.52293997 3.10024978 -0.26542025
25end
26
27task
28 energy b3lyp
29end
1basis
2 def2-svp
3end
4
5scf
6 charge 0
7 spin2p1 -1
8 type U # This is needed for TSO-DFT.
9 no_scf tso
10end
11
12scfguess
13 type fragden
14 frag 0 1 1-4 6
15 frag -1 1 5
16end
17
18mol
19 C -0.59663490 1.29366556 -0.07171644
20 H -0.18159761 1.68969864 0.84430018
21 H -0.12252870 1.52677601 -1.01427388
22 H -1.59298434 0.87532545 -0.06612308
23 Cl 0.43269073 -0.72181312 0.13298792
24 F -1.52293997 3.10024978 -0.26542025
25end
26
27task
28 energy b3lyp
29end
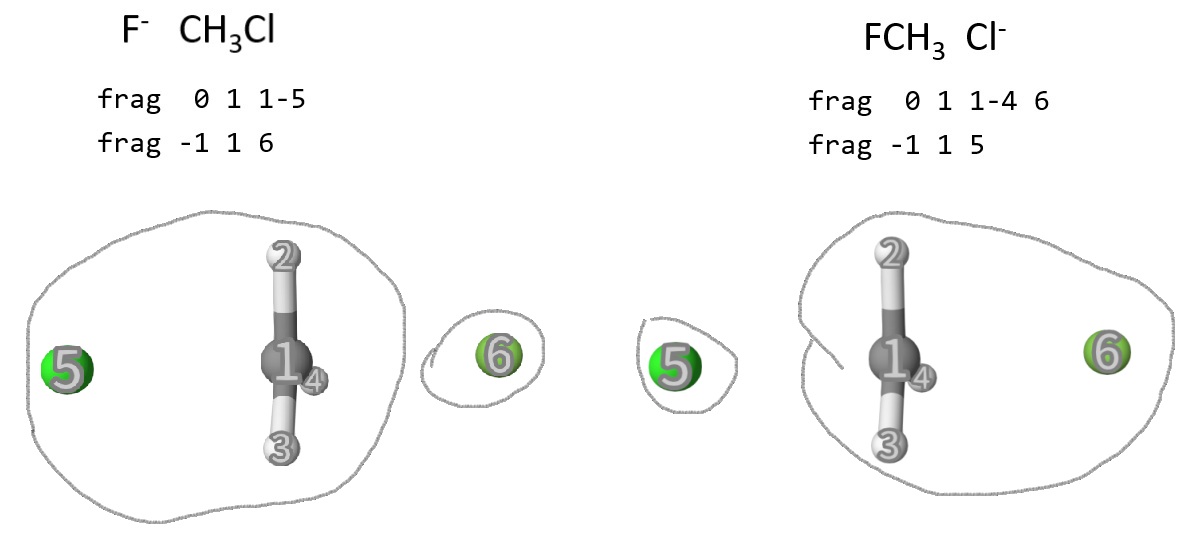
After 4 calculations, we can get the following energies in fch3cl-reac-reac/prod.out and fch3cl-ts-reac/prod.out:
Structure
Reactant Complex
Transition State
Reactant Dibatic State
-599.62530856
-599.62955746
Product Dibatic State
-599.49007047
-599.62959766
Interestingly, we observe that the reactant and product diabatic energy are the same for transition state. Acutally, this is the basis for dibatic MECP method for transition state search. See Transition State Search and mecp for more information.